Understanding Urine tests
Urinalysis is a medical test that involves analyzing a person's urine sample to assess their overall health. The test is commonly used to diagnose and monitor various health conditions, including urinary tract infections, kidney disease, and diabetes. In this post, we will discuss the different aspects of urinalysis, including the types of tests, what the results mean, and how to prepare for the test.
Types of Urinalysis Tests:
There are different types of tests that can be performed on a urine sample. The most common tests include:
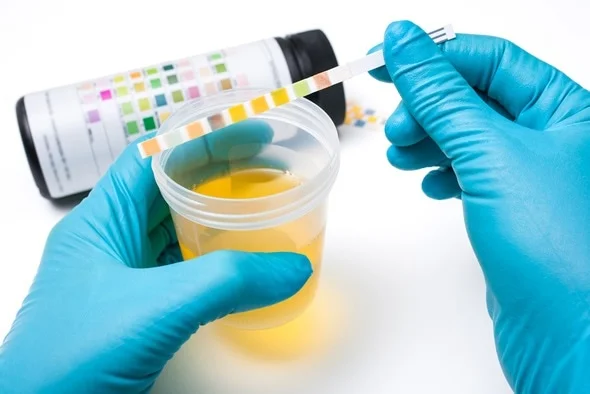
1. Physical Examination: This involves observing the urine's color, clarity, and odor. Changes in these physical characteristics can indicate underlying health issues.
2. Chemical Examination: This test uses chemical reagents to identify the presence of certain substances, such as proteins, glucose, and ketones, in the urine.
3. Microscopic Examination: This test involves using a microscope to observe the urine sample for the presence of bacteria, blood cells, and other particles that may be too small to see with the naked eye.

Interpreting Urinalysis Results:
The results of a urinalysis can provide valuable insights into a person's health status. The following are some of the key parameters that are evaluated during urinalysis and what they indicate:
1. Color: Normal urine is typically pale yellow to amber in color. If the urine is too dark, it may indicate dehydration, liver disease, or certain medications. If the urine is too light, it may indicate overhydration or other medical conditions.
2. Clarity: Normal urine should be clear. If the urine appears cloudy, it may indicate the presence of bacteria, white blood cells, or other particles.
3. Odor: Normal urine does not have a strong odor. If the urine has a strong odor, it may indicate a urinary tract infection, diabetes, or other health conditions.
4. pH: The pH level of urine is a measure of its acidity or alkalinity. Normal urine pH ranges from 4.6 to 8.0. An abnormal pH level may indicate kidney disease, urinary tract infection, or other health conditions.
5. Specific Gravity: This measures the density of urine compared to water. Normal urine specific gravity ranges from 1.002 to 1.030. An abnormal specific gravity level may indicate dehydration, kidney disease, or other medical conditions.
6. Protein: The presence of protein in urine may indicate kidney disease or other medical conditions.
7. Glucose: Elevated levels of glucose in urine may indicate diabetes or other medical conditions.
Preparing for a Urinalysis:
To ensure accurate test results, it is essential to follow specific instructions before providing a urine sample. Some of the standard preparation steps include:
1. Drink plenty of water before the test to ensure that there is enough urine for analysis.
2. Avoid eating or drinking anything that may affect the urine's color or composition, such as caffeine, alcohol, or certain medications.
3. Collect a midstream urine sample to ensure that the sample is free of contaminants.
Conclusion:
Urinalysis is a vital diagnostic tool that can provide insights into a person's overall health. Understanding the different types of tests, interpreting the results, and following the preparation instructions can ensure that the test results are accurate and meaningful. If you are experiencing any symptoms of urinary tract infections, kidney disease, or other medical conditions, consult your healthcare provider, who may recommend urinalysis as part of the diagnostic process.




0 Comments